
Net Profit Margin: What It Is & How to Calculate It

Monitoring your net profit margin is a key component in understanding how profitable your small business is and where you can trim unnecessary expenses.
It exhibits how much profit you make on every pound of revenue, after deducting all operating expenses, interest and taxes. It demonstrates the overall success of your business, which is why it is so essential to analysts and shareholders.
In this post, we’ll explain what net profit margin is, how to calculate it, what the average profit margin of UK companies is and why it’s important for small business success.
Top Tip: While we briefly touch on them below, it’s important that you have a full understanding of the various types of expenses you will incur as a small business owner before diving into the specifics of calculating your net profit margin. This way, you’ll have an easier time sticking to your predetermined business budget, which in turn will help you to identify unnecessary or excessive costs and take appropriate measures to decrease spending, improve cash flow and ultimately become more profitable. To learn more, read our guide to how to keep track of expenses💡.
Contents
- How can you calculate net profit margin?
- Net profit margin calculator
- Why is it important to know your small business’s net profit margin?
- Ways to improve your net profit margin
- Limitations of calculating net profit margin
- Expert insights
- 📹 Masterclass video: How to maximise your profits
- Wrapping up
How can you calculate net profit margin?
What is net profit margin?
Net profit margin refers to how much profit your business has generated as a percentage of your total revenue. You track your net profit margin on your income statement or profit and loss statement (P&L), which is one of the three main financial statements that you should be aware of.
Top Tip: To learn more about the three main financial statements and how to accurately record each and every one of your business expenses to gain a comprehensive overview of your costs, read our complete guide to accounting for startups 📣.
Net profit margin is calculated by dividing net profit by revenue multiplied by 100.
Before walking through how to calculate your net profit margin, it is useful to first grasp the components that affect its outcome, such as net profit, operating costs, and cost of sales.
Net profit margin formula:
Net profit margin = (net profit / revenue) x 100
What is net profit?
The net profit often refers to the ‘bottom line’. It is your business’s true profitability after accounting for all operating expenses and cost of sales.
Net profit = revenue – (cost of sales + operating costs)
Let’s say your business makes £10,000 in sales and it costs you £7,000 to make your products. You also spent an additional £1,000 on operating costs (such as taxes).
Total sales – (cost of sales + operating costs) = net profit
£10,000 – (£7,000 + £1,000) = £2,000
Net income ÷ sales = net profit margin
£2,000 ÷ £10,000 = 0.2
0.2 × 100 = 20%
Your business would have a net profit margin of 20%. Therefore, 20% of your total sales revenue is profit.
Top Tip: Paying taxes is something that every person and business must do. That said, there are several ways to reduce the amount of taxes that you pay in order to retain and inject more cash back into your business—a vital component to growing and scaling your venture. To learn more, read our guide to 8 tax breaks small businesses can take 💸.
What is revenue?
Revenue is how much your company makes during a specific time period. Your total revenue is calculated by multiplying the price of your products or services by the number of units or amount sold.
What are cost of sales?
The cost of sales, or cost of goods sold (COGS), refers to the direct cost of the materials and labour used to produce your product. It includes the costs of:
- Hosting
- Raw materials
- Transporting the goods to their present location
Top Tip: While cost of sales is relatively straightforward to understand, it can be quite difficult to calculate, depending on the types of products or services you sell and whether or not they are direct or indirect sales. To learn more about what to include in your cost of sales, how the cost of sales formula works and to read some expert insights into the process, read our guide Cost of sales: what you need to know for your business ✅.
What are operating expenses?
Operating expenses refer to the total expenses not directly associated with production but incurred in your business’s day-to-day activities. It includes:


What is gross profit?
The gross profit is the revenue your company earns minus the cost of sales. The difference between gross profit and net profit is that gross profit does not deduct all other operating expenses. It is displayed in an absolute pound amount.
Gross profit margin = (company revenue – cost of sales) / company revenue
What is gross profit margin?
Gross profit margin also presents revenue minus cost of sales but is displayed as a percentage, rather than an absolute pound amount.
While it encompasses the same meaning as gross profit, the gross profit margin has far more useful analytical and comparative significance.
We won’t dive into the details of the gross profit margin in this article, but it is beneficial to utilise as an alternative tool for assessing your company’s overall health.
Net profit margin calculator
Our net profit margin calculator measures your company's profitability in relation to its total revenue, or in other words how much of each pound received by your business is net profit.
£ £ %Why is it important to know your small business’s net profit margin?
Knowing your small business’s net profit margin will help you understand how your sales translate into profit. This knowledge is essential in making informed decisions regarding your company’s operational success and assists with forecasting future profit margins. It also helps you compare your business to others in your industry, regardless of size, which is useful when conducting market research as needed.
A drastic decline in your net profit margin is a signal that it is time to do a financial analysis and assess which areas of your company need attention to improve the margin.
Top Tip: A cash flow forecast helps you to estimate and record how much money will move in and out of your business over a 12 month period. Some of the benefits of maintaining a cash flow forecast are to predict surges or shortages in cash flow, make better business decisions (i.e. if you truly have the cash to hire new talent or begin building a new product), plan for loans or lines or credit and provide key information and context to stakeholders. To learn more, read our complete guide to cash flow forecasting 📈.
Ways to improve your net profit margin
If you have a low or negative net profit margin, you can potentially increase your small business profitability by reducing your costs or increasing your net sales. Here are a few ways that you could realistically do that:
Increase your revenue. You could review your pricing strategies and change the price of your product(s) or improve your marketing efforts.
Top Tip: Learn more about how to find a sustainable price for your products, as well as the best pricing models to stay competitive and achieve success in our 6-step-guide on how to price a product and achieve profitable markups ⚡️.
Reduce your cost of sales. Find cheaper suppliers for your goods, negotiate better deals with vendors, or trim down packaging for cheaper postage costs.
Reduce your operating expenses. Evaluate your ROI expenses akin to client dinners, work conferences, and so on, and trim down where necessary.
Reduce your interest expenses. You could transfer your money to an instrument that produces a better yield, or prioritise paying dues over other expenses to avoid hidden fees or penalties. For example, if you’re paying off a loan with a high interest rate, look to transfer the balance to another provider with a lower repayment interest rate.
Top Tip: On the tax front, a good accountant can likely help you find ways to cut down your tax bill by finding additional tax deductions and taking advantage of incentives. If you’re not exactly sure of the differences between a bookkeeper and an accountant and how they can respectively help your small business, read our guide to the difference between an accountant and a bookkeeper 🔍.
These measures will help you increase your revenue and decrease your costs, which in turn should lead to a higher profit margin.
What profit margin should a business make in the UK?
Data taken from the Office of National Statistics demonstrates that the average profit margin of UK companies during the third quarter of 2019 was:
- 9.3% for private non-financial corporations
- 9.4% for manufacturing companies
- 14.9% for companies that provide services
Legal and General’s State of the Nation’s SMEs report splits the average small business profit in the UK into three categories:
- Newer businesses, that is businesses that are two years old or less. 51% of these businesses have a net profit of £50,000 or less.
- Maturing businesses, that is businesses that are between three and 10 years old. These turn an average profit of £261,000.
- Established businesses, that is businesses that are 10 years old or older. These turn an average profit of £342,000.
Since the net profit margin is a percentage rather than a specific amount expressed in pounds, it is possible to compare the profitability of two or more businesses regardless of size.
This can tell you how well you’re doing in your industry and inform potential investors if you’re generating enough profit to cover your costs.
Top Tip: The best way to get an investor’s attention is to produce a comprehensive business plan that gives financiers the details they need to make an informed decision. To learn more, read our complete guide to how to create a winning business plan 📌.
Limitations of calculating net profit margin
It is important to keep in mind that the net profit margin is just one metric and that it doesn’t tell the whole story of how your business is doing.
It is also key to look at other metrics from your income statement too, such as cash flow or gross profit margin, as discussed earlier. Let’s have a look at two limitations of focusing on net profit margin as a measure of success.
Limitation #1: Comparing companies
The net profit margin is usually calculated to compare the performance of two companies. However, companies in different industries may have two completely different business models.
For example, a jewellery company that sells a few expensive products may have a much higher profit margin compared to a supermarket that sells many budget-friendly products.
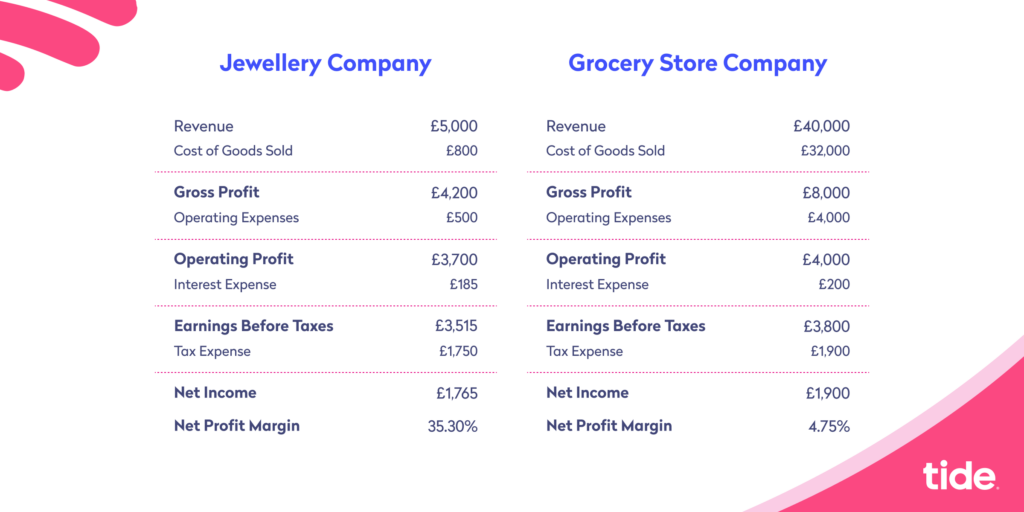
Comparing these two companies would be pointless, as they have completely different operations and belong to different industries. Therefore, you must strive for a profit margin that helps you reach your revenue and profit goals.
Limitation #2: Profit manipulation
A small business owner may choose to reduce long-term expenses by cutting corners on business essentials such as accounting or rent, to increase their profit in the short-term.
This can be misleading and make the profit net margin look deceptively healthy to potential investors. This is known as “income smoothing” or “profit manipulation.” According to AccountingCoach, incoming smoothing “refers to reducing the fluctuations in a corporation’s earnings. Income smoothing can range from good business methods to fraudulent reporting.” You can learn more about this in their article on the subject.
💡Expert insights
Insights author: Amarjeet Hans is a Senior Consultant at Crystal Clear Business Consultants, providing small and medium sized businesses with the direction, growth and stability they need to succeed.
Why is it important to know your Gross profit margin as a small business owner?
Gross profit margin is the percentage of revenue you retain after accounting for costs of sales. The figure is very common and much needed as a basic means of measuring your business profit.
For a small business, gross profit simply shows how much money you make against the cost of the product so you can project and interpret profit potential and contribution to your other expenses of running the business.
What is a good net profit margin?
Net profit margin is the percentage of revenue remaining after all operating expenses, interest, taxes have been deducted from a company’s total revenue.
A good margin will vary considerably by industry and size of business, but as a general rule of thumb, a 10% net profit margin is considered average, a 20% margin is considered high (or “good”), and a 5% margin is low.
📹 Masterclass video: How to maximise your profits
One of the key traits of successful businesses is that they make the most of the money they generate.
In this Tide Masterclass, you’ll learn new and interesting ways to maximise your profit. You’ll hear our speakers discuss:
- How to create a sales funnel 💸
- How to improve your communications with customers 📣
- How to enhance your marketing 💻
- How to increase your productivity 📈
Our speakers
- Finlay Everington
Practice Manager at SAS Micro
SAS Micro are a Tide accounting partner. - Sarah Chappell
Commercial Director at Guerillascope - Emma Lloyd
Tide member, Founder of BIG little LDN - Andi Jarvis
Tide member, Founder and Strategy Director at Eximo Marketing
Wrapping up
Wholly understanding your net profit margin is key to your business’s overall success and profitability.
Tracking this number enables you to better assess when it’s a sensible time to adjust your operating costs and cost of sales, and when to focus on increasing revenue. Making such operational changes will help to increase the net profit margin over time, which will better position your company for investor approval and long-term prosperity.
Further Reading
6 steps on how to price a product and achieve profitable markups
Photo by helloquence, published on Unsplash






